Chapter 6 - Understanding Input
September 13th, 2016.
Understanding Input. What defines an input? An input basically is any data and instructions entered into the memory of a computer. Furthermore, instructions can be entered into the computer in the form of programs, commands, and user responses.An input device is any hardware component that allows users to enter data and instructions into a computer.
The Keyboard
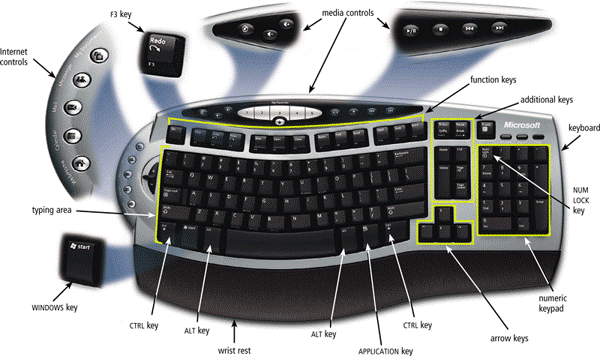
A keyboard is an input device that contains keys users press to enter data and instructions into a computer.
Fun-fact, did you know that most desktop computer keyboards have between 101 and 105 keys? Most desktop keyboards also have a numeric keypad on the right side of the keyboard. It also have function keys, CTRL keys, ALT keys, and arrow keys. Besides those, WINDOWS key, APPLICATION key, and toggle can also be found on most desktop computer keyboards.
The insertion point, also known as the cursor, is a symbol on the screen that indicates where the next character you type will appear. In other words, it is also known as the mouse cursor.
Keyboards come in many variety. Generally, there are still only two types of keyboards, which are the wired keyboards (USB) and the wireless keyboards (Bluetooth/IrDA).
An ergonomic keyboard, however, has a special design which reduces the chance of wrist and hand injuries. Ergonomics incorporates comfort, efficiency, and safety into the design of the workplace.
Pointing Devices
A pointing device is an input device that allows a user to control a pointer on the screen. A pointer however is a small symbol on the screen whose location and shape change as a user moves a pointing device.Mouse
A mouse is a pointing device that fits under the palm of your hand comfortably. It can either be wired or wireless.
Other Pointing Devices
A trackball is a a stationary pointing device with a ball on its top or side. Normally used for scrolling up and down a webpage.
A touch-pad is a small, flat, rectangular pointing device that is sensitive to pressure and motion. Examples are those that are normally present on a laptop.
A pointing stick is a pressure-sensitive pointing device shaped like a pencil eraser that is positioned between key on a keyboard. Something like this:
Touch Screens and Touch-Sensitive Pads
Generally, there are two types of touch sensitive surfaces. Which are:
Microsoft Surface
Touch-sensitive pads
Pen Input
With pen input, you touch a stylus or digital pen on a flat surface to write, draw, or make selections.
Game Controllers
Video games and computer games use a game controller as the input device that directs movements and actions of on-screen objects. Such as:
- Gamepads
- Joysticks and Wheels
- Light guns
- Dance pads
- Motion-sensing controllers
Digital Cameras
A digital camera is a mobile device that allows users to take pictures and store them digitally. Studio cameras, field cameras, and point-and-shoot camera are examples of a digital camera.
There are two factors that affect the quality of digital camera photos:
Resolution
- Resolution is the number of horizontal and vertical pixels in a display device.
- A pixel is the smallest element in an electronic display.
Number of bits stored in each pixel
- Each pixel consists of one or more bits of data.
- The more bits used to represent a pixel, the more colours and shades of gray that can be represented.
Voice Input
Voice input is the process of entering input by speaking into a microphone. Voice recognition however is the computer's capability of distinguishing spoken words.
Audio input is the process of entering any sound into the computer. Sounds includes speech, music, sound effect, and many more.
Video input is the process of capturing full-motion images and storing them on a computer's storage medium.
A Web cam is a type of digital video camera that enables a user to capture video and still images, send e-mail messages with video attachments, add live images to instant messages, broadcast live images over the Internet, and to make video telephone calls.
A video conference is a meeting between two or more geographically separated people.
Scanners and Reading Devices
There are 4 types of scanners and reading devices that we learnt, which are:
- Flatbed
- Pen or Handheld
- Sheet-fed
- Drum
Optical character recognition involves reading characters from ordinary documents. A turnaround document is a document you return to the company that creates and sends it.
Optical mark recognition reads hand-drawn marks such as small circles or rectangles. An OMR device scans the documents and matches the patterns of light.
Magnetic stripe card readers read the magnetic stripe on the back of cards such as:
- Credit cards
- Entertainment cards
- Bankcards
- Other similar cards
Bio-metric Input
Bio-metrics authenticates a person's identity by verifying a personal characteristics, such as;
- Fingerprint reader
- Face recognition system
- Hand geometry system
- Voice verification system
- Signature verification system
- Iris recognition system
- Retinal scanners
Input Devices for physically Challenged Users
Several input devices are available to assists physically challenged users, such as the keyguard, keyboards with larger keys, on-screen keyboard, various pointing devices, head-mounted pointer, gesture recognition, and computerized implant devices.